About the project
The LIID Project is very important for the development of the Republic of Serbia because it enables an even and sustainable development of local communities. Through investments in infrastructure, as well as improvement of institutional capacities, LIID encourages economic activity and improves the quality of life of citizens in all parts of the country.
Development goals of the Project

The project is implemented by the Government of the Republic of Serbia, with support from the World Bank and the French Development Agency (AFD). The planned funds, totaling €265.2 million, will be directed to local self-governments across Serbia to implement investment projects in road infrastructure, non-motorized transport, overall mobility, reducing the negative impacts of climate change on infrastructure and strengthening infrastructure resilience, greening public spaces, and improving public lighting to increase traffic safety. The funds will also support the strengthening of professional capacities within local self-government units through continuous technical assistance in relevant areas.
LIID promotes a vision of well-planned, functional settlements by fostering cooperation and synergy between those who plan and shape space and those who use it every day, creating communities that serve all citizens.
LIID: Development of local communities for a better future
Watch the video about the LIID Project and discover how this initiative will improve the infrastructure and quality of life throughout Serbia.
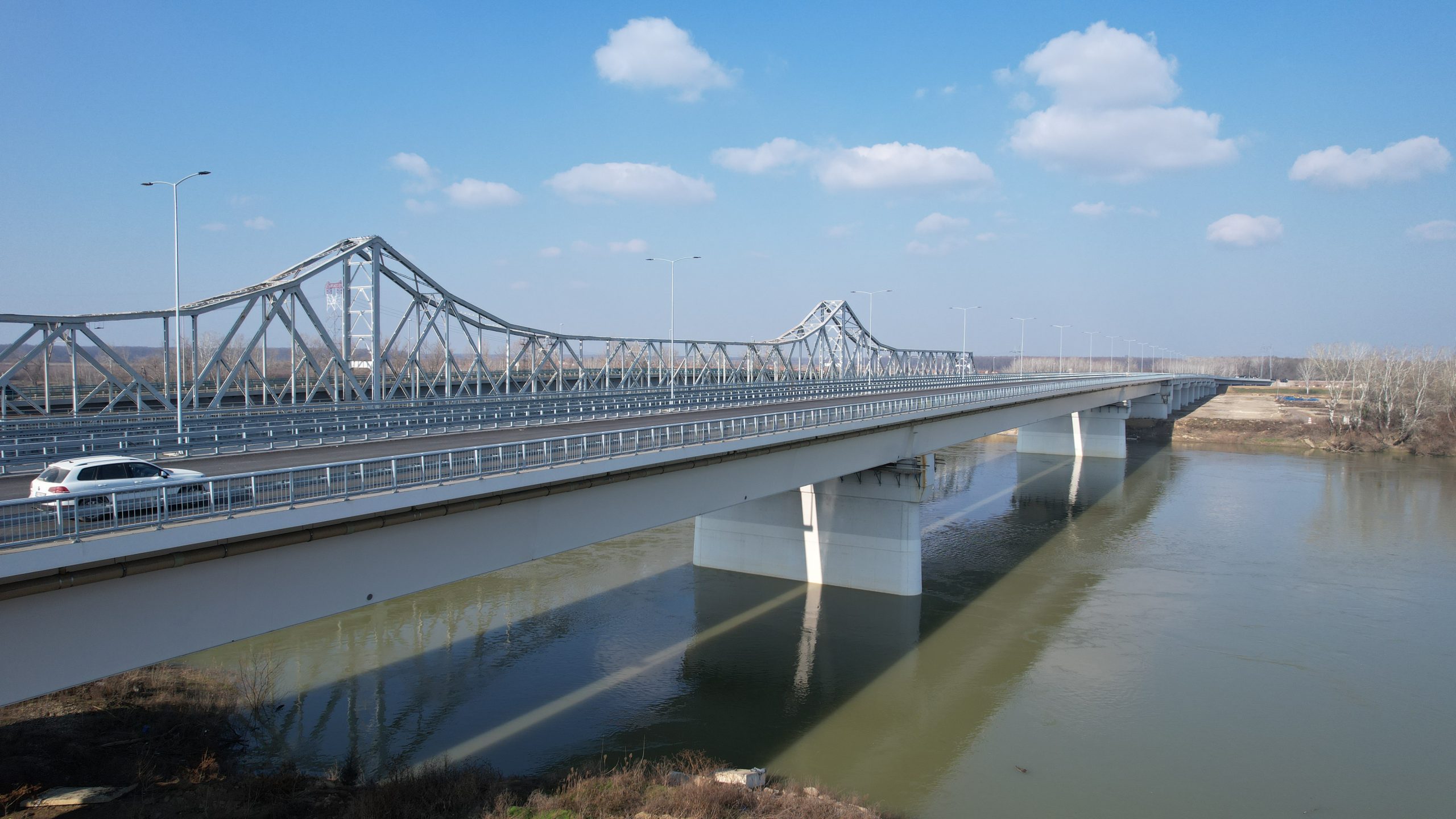


Road Infrastructure
It includes the improvement and modernization of roads, bridges and the accompanying road infrastructure, in order to improve connectivity between settlements, reduce traffic congestion and increase traffic safety. It includes the rehabilitation of the existing road infrastructure according to contemporary sustainability standards.
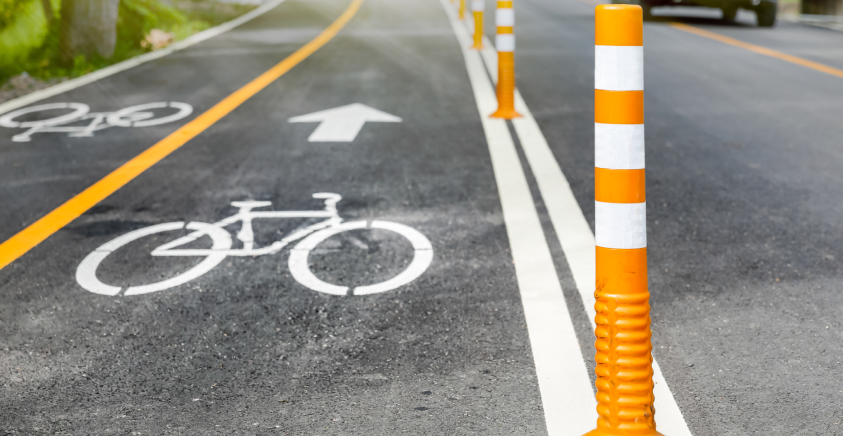


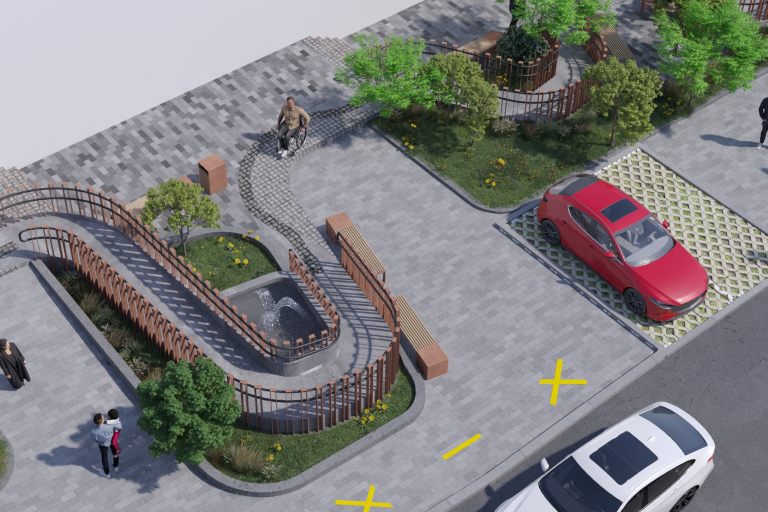
Non-motorized transport
Focuses on developing infrastructure for pedestrians and cyclists, including walkways, bike paths and sidewalks, with the goal of reducing car dependency and promoting healthy, environmentally friendly modes of transportation.
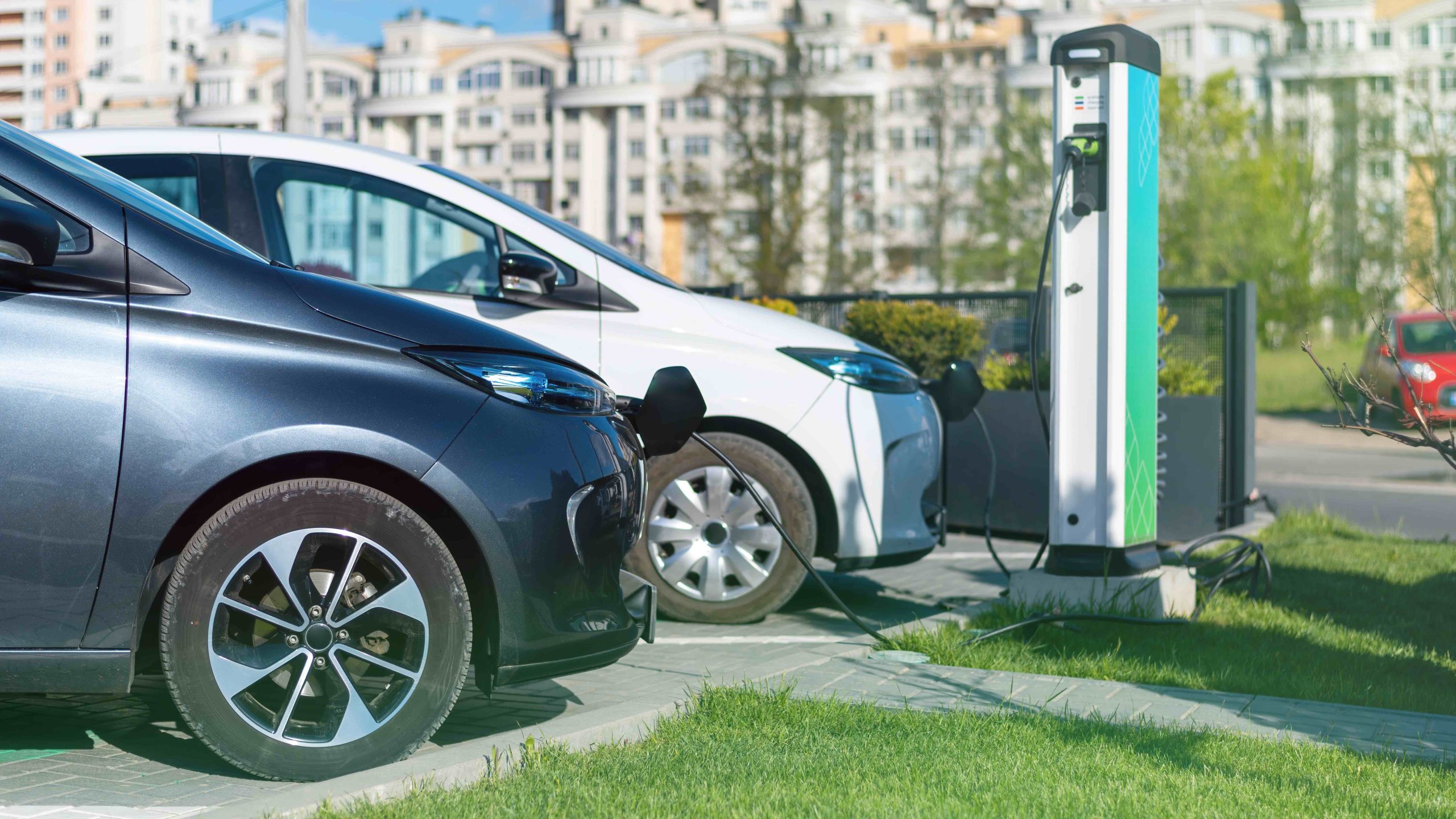


General Mobility
This component refers to the improvement of public transport, the reduction of traffic jams and the introduction of smart traffic solutions that increase efficiency and reduce the emission of harmful gases. It includes digitizing transport systems and improving accessibility to transport services for all citizens.


Climate change
Implementation of measures to increase the resilience of transport infrastructure to changing climatic conditions, improve traffic safety, reduce remediation costs, and ensure the long-term functionality of the transport network under climate uncertainty. The measures also include reducing the environmental impact of transport infrastructure by implementing climate-change mitigation actions, such as using renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies.


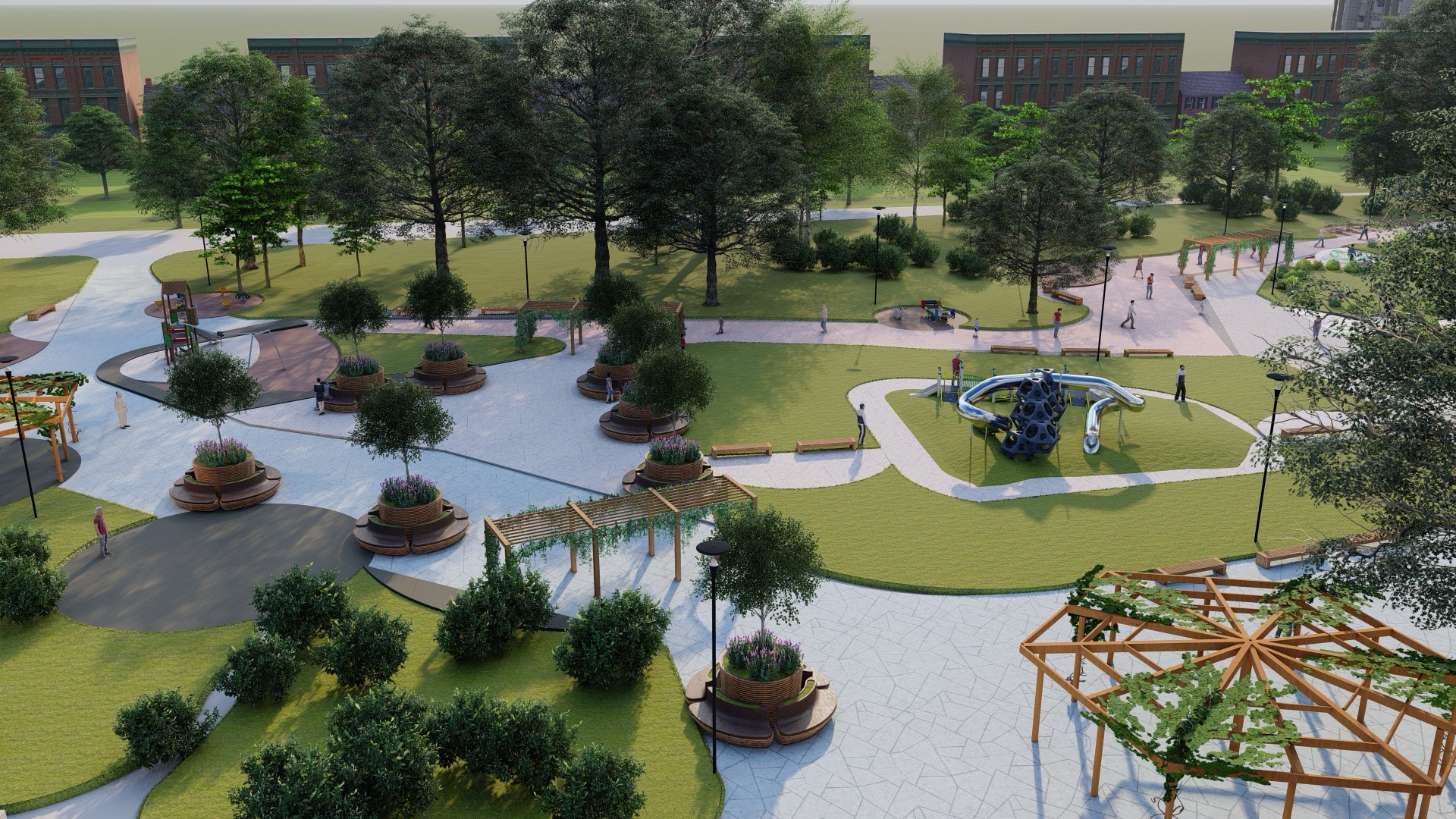
Greening of public areas
The focus is on the creation and improvement of green areas, parks and urban forests within urban areas, in order to improve the quality of life of citizens, reduce the effect of urban heat islands and increase biodiversity.
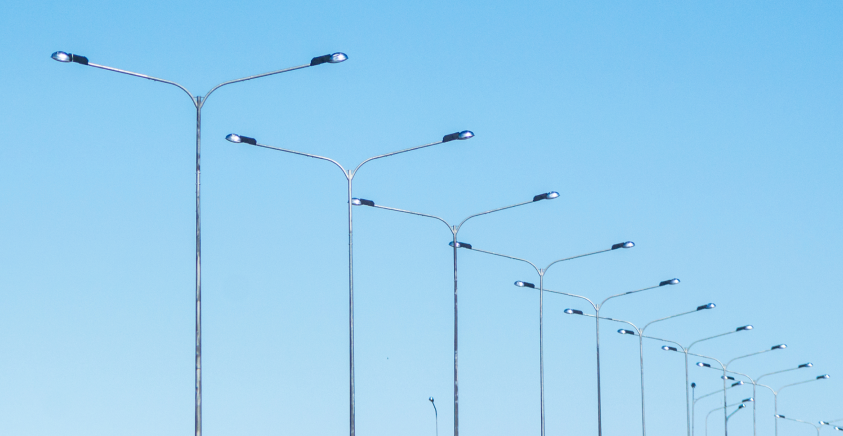

Public lighting
Modernizing public lighting by introducing LED luminaires and smart systems primarily enhances road safety: more uniform illumination, better visibility of pedestrians and cyclists, and adaptive boosting at pedestrian crossings, intersections, and in school zones. At the same time, it delivers significant energy savings and reduces light pollution, thereby lowering the overall environmental impact.

1
Component
Smart and climate-resistant mobility
The objective of this component is to improve mobility and resilience through targeted infrastructure investments, organized into two subcomponents:
1.1 Direct investments in local infrastructure, accompanied by technical assistance for construction supervision and the preparation of environmental protection plans.
1.2 Development of local road asset management systems, measures to enhance road safety for children, preparation of Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMPs), and development of smart mobility projects.

2
Component
Strengthening capacity to provide infrastructure services
This component focuses on strengthening the institutional capacities of local self-governments (LSGs) for infrastructure development through two subcomponents:
2.1 Enhancing participatory planning and the systematic identification and preparation of projects.
2.2 Providing technical assistance to improve access to funding sources, strengthen public investment management capacities, introduce and implement project management systems, and deliver staff training.

3
Component
Support to project implementation and raising awareness
The aim of this Component is to provide the necessary resources for project management and raise the awareness of the population and communities about the importance of the Project.